High-Efficiency Megawatt Motor (HEMM)
High-Efficiency Megawatt Motor
The High-Efficiency Megawatt Motor (HEMM) is a 1.4 megawatt electric machine being developed at NASA's Glenn Research Center in Cleveland to improve efficiency in future aircraft with electrified propulsion systems.
Quick Facts
The HEMM motor is 10 times more powerful than a traditional car engine.

HEMM is a partially superconducting motor enabling higher efficiency with minimal weight compared to state-of-the-art motors.

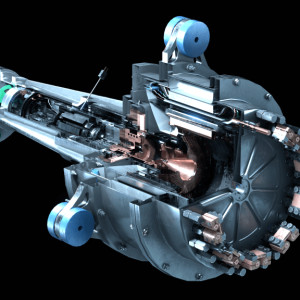
The 1.4-megawatt (MW) High-Efficiency Megawatt Motor (HEMM) is being designed to meet the needs of electrified aircraft propulsion. HEMM has a target performance of 16 kW/kg, 99% efficiency, and will have 3 times lower losses and weight than current aircraft motors and generators. The HEMM technology can be integrated with a typical aircraft cooling system and can be applied to a range of aircraft types that require megawatt-level electrical power.
New technologies must be developed to ensure the motor can produce more power per mass while efficiently maintaining required cryogenic temperatures. Three components being built and tested are a rotating acoustic cryogenic cooler, superconducting rotor coils, and a high-performance stator. HEMM's exterior looks like a standard motor, but inside, it houses advanced technologies to maintain proper function while increasing power capability.
- Stator: The stator generates current with a cable made up of 5,000 hair-thin wires.
Housing the rotor in a vacuum tube minimizes heat transfer between the stator and rotor.
- Superconducting Coils: Superconducting materials can carry more current than a common conductor, resulting in a higher-performing motor. The spinning coils must be kept at extremely cold temperatures (-223?C) to maintain their superconducting properties.
- Cryocooler: The superconducting rotor does not require an external cooling system but is cooled by an integrated cryocooler. Powered by a rapid-moving linear motor, the cryocooler maintains the cryogenic temperature limit of the rotor coils.
HEMM components are undergoing individual testing and analysis.
Once each component has demonstrated a high level of confidence, they can be manufactured for a test of the full-scale 1.4-MW High-Efficiency Megawatt Motor.
[embedded content] Learn more about advanced cryocooler thermal testing of High Efficiency Megawatt Motor (HEMM) components for future electrified aircraft propulsion.The HEMM motor is extremely powerful and efficient for its given size (16 inches by 42 inches).
Though smaller than an average car engine, the 1.4-MW motor is 10 times more powerful.
- Uses standard aircraft cooling systems
- Direct drive at optimal turbomachinery speeds (no gearbox)
- Can be shut off if fault occurs (wound field)
Researchers use the Integrated Cryogenically-Cooled Experiment Box (ICE-Box) testing rig at NASA's Glenn Research Center in Cleveland to perform tests of HEMM's superconducting rotor at specific currents and temperatures.
Learn More [1]
Explore and download a collection of publications to learn more about HEMM development and applications.

Aircraft Concepts
Learn more about NASA's conceptual aircraft design studies for future electrified aircraft.

EAP Labs and Testbeds
Learn about NASA's labs and testbeds enabling advanced electrified aircraft propulsion research.

Technology
Discover the innovative systems and technologies that enable safe and efficient electrified propulsion.
References
- ^ Learn More (www.nasa.gov)