Alformet white paper examines untapped potential of TPC electric motor sleeves
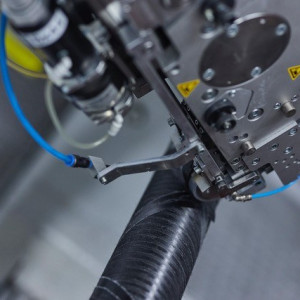

Laser-assisted tape winding (LATW) process. Source (All Images) | Alformet GmbH Alformet GmbH[1] (Dorth, Germany) announces the release of a white paper[2] exploring how thermoplastic composite (TPC) rotor and stator sleeves can enhance electric motor performance.
According to the company, growing electrification of all industries places increasing demands on electric motor performance and production. With higher rotational speeds, tighter efficiency requirements and the push for challenging solutions, conventional materials such as metals and thermoset composites reveal their limitations. Thermoplastic composites, however, present a new opportunity to optimize electric motor design.
Featured Content
What are some of the advantages to TPC sleeves?

Composite rotor/stator sleeves.
Dampening and dimensional stability. TPCs, combined with carbon fibers, offer near-zero thermal expansion and enhanced vibration damping. This improves stability at high speeds and extends motor longevity. Tight manufacturing tolerances. The laser-assisted tape winding (LATW) process ensures high-precision manufacturing directly from production, reducing the need for post-machining.
Reduced wall thickness. Optimized fiber placement through in situ consolidation in TPC sleeves enables thinner walls while maintaining strength, reducing material use and improving space efficiency. Environmental sustainability. Unlike thermoset composites, thermoplastic processing eliminates the use of harsh chemicals, making it a cleaner and more sustainable alternative with a low CO2 footprint, and materials that may be reused at the motor's end of life. Room temperature processing. Thermoplastic tape welding occurs at localized heating points, enabling direct winding onto sensitive components like permanent magnets without risking demagnetization.
Customization of material properties. With the right combination of polymer and fiber, TPCs allow control over sleeve thickness, thermal conductivity and CO2 footprint, ensuring they meet the exact requirements of different electric motor applications. Scalability and automated production. The LATW process enables high-speed, automated production of composite sleeves, ensuring consistency and cost-effectiveness in high-volume manufacturing. Alformet's white paper serves as a resource for engineers on both sides of the industry -- those in electric motor design unfamiliar with composite materials, and those in thermoplastic composites seeking to understand electric motor requirements.
Key topics covered include:
- Comparing thermoplastic composites with metals and thermosets for rotor and stator sleeves
- Design considerations to best balance design for performance, design for manufacturing, design for cost and design for assembly.
- Manufacturing insights on how automation and scalability make thermoplastic solutions viable for industrial production.
The white paper can be downloaded here[3].
Keep up with Alformet's developments at its LinkedIn page[4].
Alformet will also be at JEC World 2025 at Booth K122 in Hall 5.
Related Content
References
- ^ Alformet GmbH (www.alformet.com)
- ^ white paper (www.alformet.com)
- ^ downloaded here (www.alformet.com)
- ^ LinkedIn page (www.linkedin.com)